Ford Mustang GT 1996-2004: Gear Ratio Information
While many enthusiasts are concerned with horsepower and torque numbers, thoughts of proper gearing are often set aside. Vehicle performance can be greatly improved by optimizing gearing for your intended application.
This article applies to the Ford Mustang GT (1996-2004).
Ford Mustangs leave the factory with a well rounded mix of performance and fuel economy to meet the demands of a daily driven vehicle. The factory gear ratios in the transmission and rear-end are chosen to allow for RPM-friendly highway cruising, while still providing respectable acceleration and top speed figures. Despite these attributes, many performance enthusiasts find the stock gearing to be lackluster at best, especially in racing and performance driving environments. Fortunately, the Mustang lends itself well to gear ratio changes and, even with a stock engine configuration, can see impressive improvements in acceleration. While various drivetrain components can be changed to increase performance, most agree that choosing an appropriate final drive ratio (rear-end gearing) is one of the best modifications that can be done to any Mustang. This article will outline gear ratio information for the SN95 Mustang GT and what changes can be made to ensure you are getting the most out of your car.
Component Breakdown
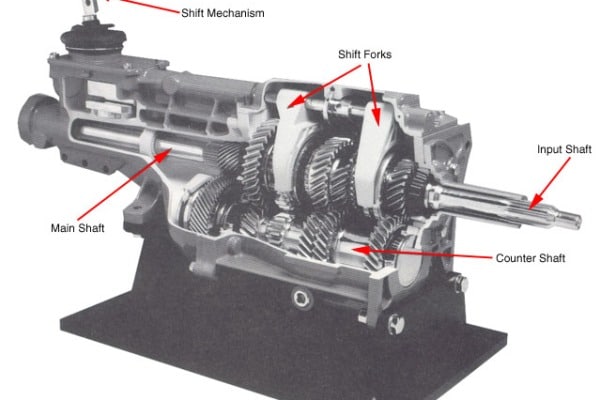
Transmission Gears
The transmission functions to transfer power from the engine to the the rear differential and eventually the wheels. The transmission is filled with numerous gearsets that multiply engine torque to a varying degree. Since engines have a limited operating range, a transmission with multiple gears must be used to allow engines to function within their optimum powerband. A transmission must allow the engine to have enough torque to accelerate in lower gears, while also providing adequate speed in higher gears and all while limiting fuel consumption. In a nutshell, a transmission operates by converting the engine power entering through the input shaft to a different speed depending on the selected gear. This altered power then exits the transmission through the output shaft and to the driveshaft/differential. Each gear has a ratio that alters the engine power to a varying degree. Lower gears can multiply engine speed by as much as 3.5:1 to allow for greater torque to accelerate the car. High gears and overdrive gears are closer to a 1:1 ratio, with the latter spinning at a speed slower than the engine RPM to allow for higher cruising speeds and more MPGs.
Differential Gears
The differential gears, also referred to as a ring and pinion, is an additional gearset located in the rear axle of the Mustang. The differential works in tandem with the transmission to supply power to the rear wheels of the car. Power from the driveshaft enters the rear-end and turns the smaller pinion gear. The pinion gear is meshed with the larger ring gear, which is attached to the differential and turns the rear axles, thus transferring power to the wheels. The differential gearset ratios installed from the factory are considered by many owners and performance enthusiasts be to a bit conservative. Swapping to a lower ratio is an inexpensive way to quickly and easily improve performance.

Figure 2. Ring and pinion. 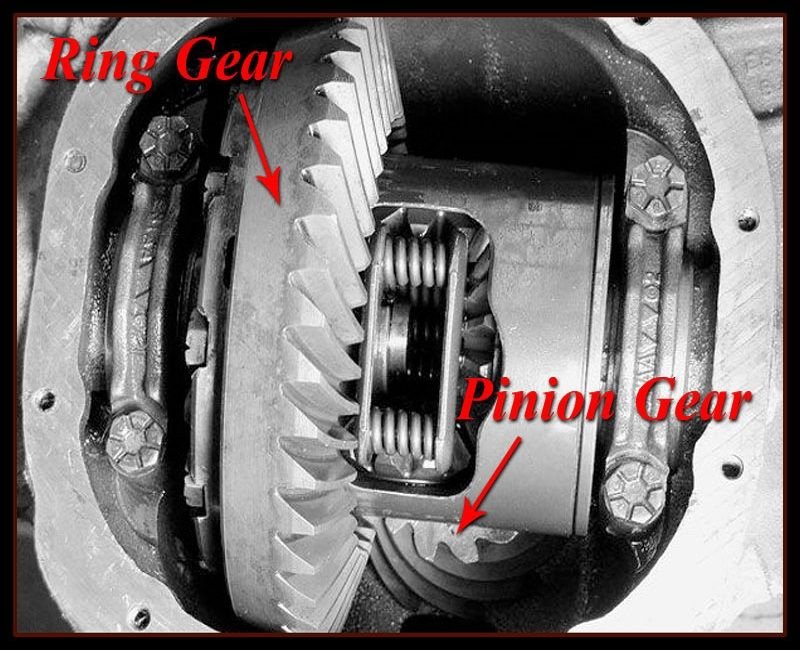
Figure 3. Installed inside the differential.
Common Questions
Should I change transmission gear ratios or rear-end gear ratios?
Generally speaking, transmission ratio swaps are much more expensive than rear-end gear ratio changes, and are typically unnecessary in 99% of all applications. Transmission gear ratio changes require complete transmission disassemble to swap cogs. Most individuals opt to replace their stock transmissions with a 6-speed unit before doing any internal transmission work (see the related article How to Install T-56 Manual Transmission). Conversely, changing gears in the rear-end is much simpler and is considered one of the most cost-effective mods that will liven up the SN95 Mustang GT.
Why should I change my rear gears?
Perhaps the biggest complaint of the 4.6L modular V8 is that is lacks a bit of low-end grunt compared to larger displacement engines. A set of higher ratio gears will slightly shorten gearing, improve acceleration, and allow the engine to be in the meat of its powerband more often.
What does the numerical rear gear numbers mean?
Most owners and parts suppliers refer to a specific rear gear set with a number such as "3.73" or "4.10." These referenced numbers are shorthand for the ratio at which the driveshaft turns compared to the rear wheels. For example, a 4.10:1 gear ratio will see the driveshaft spin just over four revolutions to allow the rear wheels to roll around one time. A higher number indicates shorter gearing.
How can I tell which rear gears my car has?
SN95 Mustang GT's typically left the factory with 2.73, 3.08, or 3.27 gears, depending on the transmission type. Perhaps the easiest way to dsitinguish which ratio you have is to jack up your car and rotate the driveshaft or wheels. By counting the number of times the driveshaft spins around to make one complete revolution of the rear wheels will indicate your ratio.
Which gear ratio is best for me?
The three most common ratios that owners often install are 3.55, 3.73, and 4.10 gears. The intended usage of your Mustang will greatly influence which gears are best suited for the car. For example, many enthusiasts choose a 3.73:1 ratio because of its versatility. A set of 3.73 gears will provide a noticeable improvement in acceleration, yet maintain reasonable fuel economy on the highway. On the other hand, a weekend only/track car that has little concern for highway manners and fuel economy may see an additional benefit to choosing 4.10 gears. The engine power output, rev limit, tire size, and equipped transmission all play a role in rear gear selection, so consider your setup before choosing a set of gears.
Will my speedometer read differently with different gears?
Whenever the tire sizes, rear gears or transmission ratios are changed, the speedometer will read incorrectly; however, the Mustang has an electronic speed sensor that can be programmed with a handheld PCM tuner. A tuner will allow individuals to correct the speedometer and odometer readings for their specific setup.
(Related Article: Engine Tuning Information - MustangForums.com)
Are there any drawbacks to installing a set of higher ratio gears?
The only real concern with changing the rear-end ratio is the effect that it will have on fuel economy. A daily driven car that sees a lot of highway usage will be best off with a more conservative ratio. Remember, the trade-off with shortening the gearing to improve acceleration is a lower top speed for each transmission gear. That being said, most enthusiast feel the performance benefits far outweigh the slight increase in fuel usage.
How much does a rear gear or transmission swap cost?
If you are handy with a wrench and have the necessary tools, a rear gear kit can be installed for about $200; otherwise, the going rate at a reputable shop is approximately $500. A 6-speed tranny can run anywhere from $2,000 to $4,000 depending if a complete kit is used or if components are pieced together. Tack on a good four to six hours of labor if you plan to have a shop do the heavy lifting.

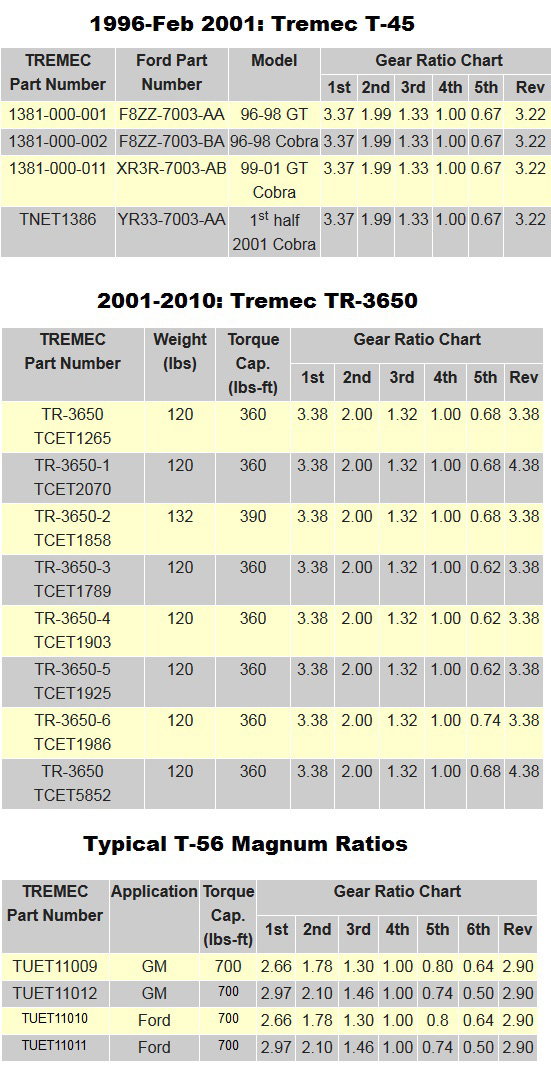
Transmission Ratio Charts
Referencing the transmission gear ratios can be helpful in deciding on a transmission swap or choosing a set of rear gears (final drive ratio).
Related Discussions
- Stock Gears vs 3.73 vs 4.10 What's the Best? - MustangForums.com
- Stock Gear Ratio on 2000 GT? - MustangForums.com
- TR-3650 Gear Ratios? - MustangForums.com






